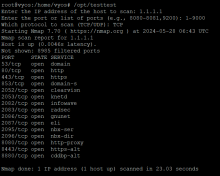
As an additional feature, nmap can be used to scan host ports or domain names. You can create a command in the main mode of the system and bind it to a script. The script scans ports from a separate file which can be updated or added at any time to the required ports.
Also VyOS has the library - import nmap
Could you accept the feature to create a pull request?
root@k:/t# ./scanport3.py Enter remote host: 1.1.1.1 Scanning completed. Open ports: Port Description 53 DNS (Domain Name System) 80 HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) 443 HTTPS (HTTP Secure) 8080 HTTP Alternate Closed ports: Port Description 21 FTP (File Transfer Protocol) 22 SSH (Secure Shell) 23 Telnet 25 SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) 110 POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3) 123 NTP (Network Time Protocol) 143 IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) 465 SMTPS (SMTP Secure) 500 IPSec VPN (Internet Protocol Security) 587 SMTP (Submission) 993 IMAPS (IMAP Secure) 995 POP3S (POP3 Secure) 1433 MS SQL Server 1521 Oracle Database 1701 L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) 1723 PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) 3306 MySQL 3389 Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) 5432 PostgreSQL 5900 VNC (Virtual Network Computing)